|
⇐ Previous Article — Table of Contents — Next Article ⇒
New Energy Times home page
Anonymous* Mechanical Engineer's Analysis of
Thermal Dispersion of Hose and Vapor Speed Analysis
Appendix 4 to New Energy Times Report #3
This is an analysis of the predicted thermal dispersion of heat along a 5-meter hose. This analysis shows that thermal dispersion of heat in an outlet hose similar to that used in Andrea Rossi's device will contribute only a very small reduction in the output velocity of the steam.
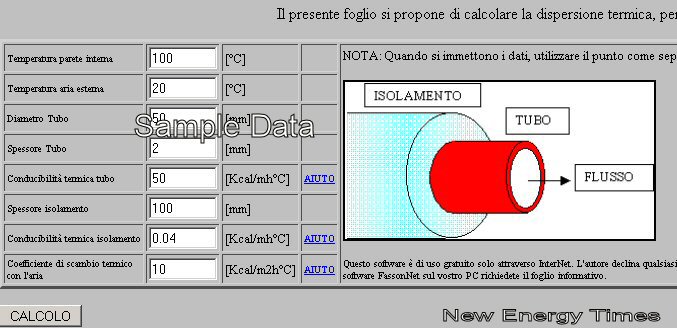
At this Web address, http://web.tiscali.it/fassonnet/term/ca_tub.htm, there is a program for calculating the dispersion of hose. I used the following information:
Conducibilità termica tubo (hose thermal conductivity):
0,22 W/(mK) = 25 Kcal/mh°C
Conducibilità termica isolamento (insulation thermal conductivity):
25 Kcal/mh°C
Coefficient of heat exchange with the air:
20-25 -> average: 22 Kcal/m2h
This parameter is not easy to define because the tube has a small diameter. The
values 20 to 25 are acceptable values.
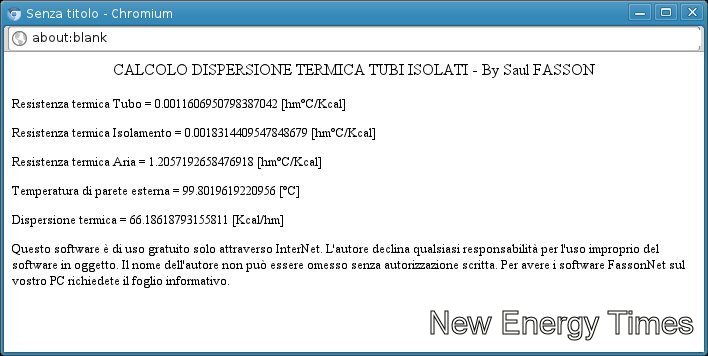
The result is 66 Kcal/hm converted to watts: 66*4186/3600 = 76 watts/m
If the hose is 5 meters long, the value is 383 watts.
That heat loss of the hose is compensated, reducing 10% dryness of vapor; for
example, if the steam has 90% dryness, as Rossi says, the quality out of
the tube is reduced to 80%, and the output speed is reduced by only 4 m/sec. So
from 40 m/s, the speed is reduced to 36 m/s, based on Rossi's claim.
* Author Information (Italy)
The author of this report has a degree in mechanical engineering. He works as a computer consultant, specifically as an advanced technology adviser, particularly in the renewable-energy sector. He has asked to remain anonymous. We agreed because we have confirmed his identity, we consider his information useful, and Rossi has recently publicly threatened and attempted to intimidate several qualified critics.
⇐ Previous Article — Table of Contents — Next Article ⇒
| 
